Common menu bar links
Breadcrumb Trail
Institutional links
Chief Information Officer Branch
IT Project Review and Oversight
Enhanced Management Framework
ARCHIVED - A Guide to Effective Business Continuity in Support of the Year 2000 Challenge
 This page has been archived.
This page has been archived.
Archived Content
Information identified as archived on the Web is for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. It has not been altered or updated after the date of archiving. Web pages that are archived on the Web are not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards. As per the Communications Policy of the Government of Canada, you can request alternate formats on the "Contact Us" page.
Appendix D - Business Function Prioritization Approach
1. How to Prioritize Business Functions
To prioritize business functions, departments must utilize a business model that accurately identifies all the functions performed by the organization (Appendix C - Functional decomposition approach). Once assigned a unique function identifier, business functions can then be prioritized using pre-determined criteria. Within the context of the Year 2000 Project, these criteria should be those provided by TBS to determine the "mission-criticality" of specific government functions (i.e. when using the TBS criteria, the higher the function scores the more "mission-critical" it is).
2. Score Business Functions
2.1 Process
The prioritization process consists of scoring functions, found at the lowest level of the business model, based on the TBS criticality criteria and developing a prioritized list of functions that will provide the required framework to structure and sequence business continuity activities.
The total score of a given function is achieved as follows:
- using the criteria found in Section D-1, functions should be scored against each criteria on the basis of their ability to have the identified impact. For example, the function "Pay employee" may score low on the criteria dealing with safety and environment but would score higher on economic well being of Canadians and employee morale;
- the proposed scale to score each function against the criteria
is as follows:
Low = 1 Medium = 3 High = 5
-
2 and 4 are used as intermediate values. 0 is used when the function does not have an impact in this area (Impact on safety, environment, etc.).
- to score a function, individuals should ask themselves: "Is the impact's likelihood for a given function low, medium, or high? They would then assign a score from 1 to 5 based on their best judgement (this approach respects the risk concepts because the weighting factor represents the impact and the scores the probability); and
- the weighting factors are applied to the total score achieved by a function in a given category. For example, if the total score of a function in the "Impact on Canadians" category is 25, this score would be multiplied by 5 to include the weighting factor assigned to this category. The scores from each category of criteria are then added to obtain the overall score for a given function.
2.2 Deliverable
The deliverable for this activity is a prioritized list of business functions.
3. Techniques and Tools
This table provides a summary of the techniques and tools used for this activity. Details of the techniques and tools can be found in the appropriate sections.
Table D-1: Business Function Prioritization Techniques and Tools
|
Activity |
Techniques and Tools |
| Score Business Functions |
|
4. Guidelines and Tips
The following are guidelines and tips that can facilitate the performance of this activity.
- Get function owners to score their respective functions against criteria, use groups to confirm the final ranking;
- Use workshops with all functional areas to achieve the final list; and
- Involve the governance structure quickly, as most organizations have not been culturally good at doing cross-functional business function prioritization, to make decisions.
The following table summarizes the criteria used to assess business functions as defined by the Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat. Weighting factors from 5 (High) to 1 (Low).
Table D-2: Mission-critical Criteria
|
Criteria |
Weight |
Definition |
| Impact on Canadians |
5 |
These criteria lead to the establishment of a government-wide mission-critical function. A government-wide mission-critical function has been defined as a service or function performed by a federal government department or agency: |
|
||
|
Impact on the health/environment of Canadians. Sample business functions associated with this criteria include food inspection, drug management and testing, and other related functions from the "Health Canada" portfolio. | |
|
Impact on the safety of Canadians. Sample business functions associated with that criteria include search and rescue functions. | |
|
Impact on the security of Canadians. Sample business functions associated with that criteria include law enforcement, correctional services, and other related functions from the Solicitor General's portfolio. Defence related functions are also associated with this criteria. | |
|
Impact on the economic circumstance of Canadians. Sample business functions associated with that criteria include Receiver General functions, Pension, Welfare, and other functions that provide economical benefits to Canadians. | |
|
Impact on the environment of Canadians and Canada. Sample business functions associated with that criteria reside within Environment Canada, environmental response groups in Fisheries and Oceans. | |
| Impact on Obligations |
3 |
These criteria lead to the establishment of a department-wide mission-critical function. Within the context of this guide, a department-wide mission-critical function has been defined as a service or function performed by a federal government department or agency: |
|
||
|
Self-explanatory | |
|
Self-explanatory | |
|
Self-explanatory | |
|
Within the Federal government. | |
|
Provincial, Regional, Municipal governments. | |
|
Self-explanatory | |
| Impact on Employees |
1 |
|
|
Self-explanatory | |
|
Self-explanatory | |
|
Self-explanatory | |
| Financial Impact |
1 |
|
|
Impact on Federal government where revenue or operating expenditure is affected, or cost is increased. | |
|
Self-explanatory |
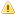
Section D-2: Sample Prioritized Function List
| ID | Code | Function Name | Relative Score | Raw Score | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.1.2 | SAR | Detection of distress alters | 1 | 169 | GWMC |
| 5.1.5 | SAR | SAR coordination | 0,99 | 168 | GWMC |
| 5.1.4 | SAR | Search and rescue planning | 0,98 | 166 | GWMC |
| 3.1.1 | MCTS | Detect and respond safety/distress calls | 0,94 | 159 | GWMC |
| 3.1.2 | MCTS | Respond to calls | 0,94 | 159 | GWMC |
| 3.1.3 | MCTS | Analyze situation | 0,94 | 159 | GWMC |
| 3.1.4 | MCTS | Alert proper agencies | 0,94 | 159 | GWMC |
| 3.1.5 | MCTS | Coordinate information process | 0,94 | 159 | GWMC |
| 3.1.8 | MCTS | Receive safety information from outside sources | 0,94 | 159 | GWMC |
| 3.1.9 | MCTS | Broadcast safety information | 0,94 | 159 | GWMC |
| 5.1.1 | SAR | Ensure SAR coverage by ressources | 0,82 | 139 | GWMC |
| 2.2.2 | MNS | Provide electronic aids to navigation | 0,80 | 135 | GWMC |
| 5.2.2 | SAR | Environmental response operations | 0,79 | 133 | GWMC |
| 5.3.2 | ER | ER contingency planning exercising | 0,79 | 133 | GWMC |
| 2.1.3 | MNS | Overflow outpout/forecast/control | 0,77 | 130 | GWMC |
| 2.1.4 | MNS | Water level forecasting | 0,77 | 130 | GWMC |
| 4.2.2 | ICE | Ice routing and dice charts info | 0,77 | 130 | GWMC |
| 4.4.1 | ICE | Monitoring of ice conditions | 0,77 | 130 | GWMC |
| 4.4.2 | ICE | Icebreaking for flood control | 0,77 | 130 | GWMC |