Common menu bar links
Breadcrumb Trail
ARCHIVED - Hazardous Materials Information Review Commission - Report
 This page has been archived.
This page has been archived.
Archived Content
Information identified as archived on the Web is for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. It has not been altered or updated after the date of archiving. Web pages that are archived on the Web are not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards. As per the Communications Policy of the Government of Canada, you can request alternate formats on the "Contact Us" page.
Section II – Analysis of Program Activity by Strategic Outcome
Strategic Outcome
Trade secret exemptions are provided in a way that balances the right of industry to protect their confidential business information with the right of workers to receive accurate information concerning the health and safety hazards posed by chemicals in the workplace.
Program Activity by Strategic Outcome
| 2009-10 Financial Resources ($ thousands) |
2009-10 Human Resources (FTEs) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planned Spending |
Total Authorities |
Actual Spending |
Planned | Actual | Difference |
| 5,555 | 5,986 | 5,845 | 54 | 49 | 5 |
| Expected Results |
Performance Indicators |
Targets | Performance Status |
Performance Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Claimants are able to sell their products without disclosing confidential business information within an appropriate amount of time |
Percentage of claims registered within 7 days |
100% |
Met all |
100% |
|
Workers are provided with corrected health and safety information within an appropriate amount of time |
Percentage of claims for which the elapsed time between the registration of the claim and the issuance of the decision and order in within the target period |
90% within 365 days |
Not met |
42% 4 |
|
Disputes are resolved prior to appeal |
Percentage of disputes resolved prior to appeal |
100% |
Met all |
100% |
4 42% is due to a backlog of claims that is on target to be eliminated by 31 March 2011.
Benefits for Canadians
Canada's public health system exists to safeguard and improve the health of Canadians. The responsibility for public health is spread across the federal, provincial and territorial governments. Occupational health and safety programs, including WHMIS, are an essential part of the Canadian public health system. As part of WHMIS, the Commission provides the trade secret exemption mechanism on behalf of the federal, provincial and territorial governments, including the related occupational health and safety aspects in order to protect Canadian workers. It does this by assessing and addressing the hazards of chemicals used in the workplace, by innovation in translating its knowledge of hazard classification and communication, by ensuring compliance with public standards across jurisdictions, and by fostering mutual support and cooperation among key stakeholders. Through these activities HMIRC enhances public health and safety and the autonomy of citizens to make informed health and safety choices, which contributes to the achievement of the Government of Canada strategic outcome of "Healthy Canadians". The Commission's work also supports the Government of Canada's strategic outcome of a "Fair and Secure Marketplace" by promoting intellectual property rights, and economic growth and prosperity. This outcome ensures the marketplace continues to foster competitive conditions in order to attract investment, encourage innovation, and protect the public interest. The Commission enhances competitiveness by protecting trade secrets in the chemical industry.
Performance Analysis
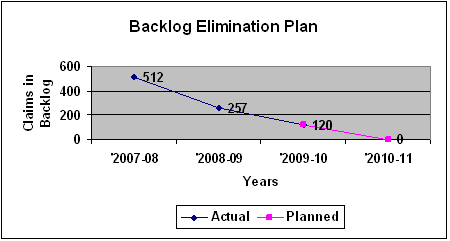
The Commission's Program Activity, the Claim Exemption Process, surpassed the targeted reduction in backlog claims. The backlog was reduced by 137 to a remainder of 120 claims and represents an accumulated reduction of 76.6% to date (See Table 2 and Figure 1). Eliminating the backlog will significantly reduce the time between registering a claim and issuing a decision, providing workers access to corrected health and safety information faster.
In 2009-2010 the program repeated last year's success in registering 100% of claims within 7 days. In addition, the Commission's review of claim validity and MSDS compliance showed increased efficiency with 42% of reviews completed within 365 days. With the elimination of the backlog of claims in 2010-2011, the Commission anticipates significant future efficiencies in this area.
Over time the Program Activity will gradually reflect the benefits of several initiatives that have been or are in the process of being implemented. A case in point is the new streamlined claim process based on amendments to HMIRC legislation for which the first claims to make it through the entire process are just now reaching completion. Other initiatives that will contribute to improved results include electronic tools and the revised screening manual.
Table 2
| Backlog of Claims at March 31, 2008 | 512 |
| Backlog of Claims at March 31, 2010 | 120 |
| Backlog Reduction (%) | 392 (76.6%) |
Figure 1
The Commission processes claims on a priority basis, using criteria such as the nature of the hazard present. This supports the goal of delivering important, necessary health and safety information to Canadian workers as fast as possible while protecting the chemical industry's confidential business information. In 2009-2010, high-priority claims represented 51% of total claims processed. A review of identified MSDS violations indicates the type and percentage of errors that were identified and subsequently corrected in order to reach the workplace without delay (See Table 3). Corrections made to accurately reflect hazard information on an MSDS can have significant correlation and application to other MSDSs prepared by the same claimant; the Commission would like to more actively promote this use of its scientific expertise in the future.
Table 3
| Violations Category | Number of Violations in 2009-2010 |
Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Toxicological Properties | 274 | 25.3 |
| Hazardous Ingredients | 254 | 23.4 |
| Headings/Format, etc. | 160 | 14.8 |
| First Aid Measures | 148 | 13.6 |
| Physical Data | 63 | 5.8 |
| Fire or Explosion Hazard | 46 | 4.2 |
| Hazard Classification | 42 | 3.9 |
| Preparation Information | 38 | 3.5 |
| Reactivity Data | 29 | 2.7 |
| Product Information | 22 | 2.0 |
| Preventive Measures | 9 | 0.8 |
| Total | 1085 | 100 |
| Number of claims | 257 | |
| Average number of violations per claim | 4.2 |
Lessons Learned
During 2009-2010 the Commission has been intensely engaged in the development of an integrated plan to align strategic and operational plans. This plan reflects the three renewed strategic directions defined and endorsed by the Commission's Council of Governors in October 2009 that emphasize 1) proactive compliance, 2) knowledge translation and dissemination, and 3) strategic partnerships. One of the intentions of these strategic directions is to exploit HMIRC's unique knowledge and expertise regarding hazard communications through outreach and partnerships.
Other key organizational tools under development in conjunction with the integrated plan are: 1) a Logic Model, a chart displaying the horizontal and vertical relationships between Commission activities, strategies and target group, and 2) an Evaluation Framework, which will respond to a key recommendation in the last Treasury Board MAF assessment. An HR Strategy has already been developed to address key staffing issues such as recruitment, retention and training especially in the context of a small agency with limited resources and opportunities for career development, as well as the significant number of staff who are eligible for retirement. Consideration will be given to identifying key positions and succession planning, as well as training, mentoring, coaching and job rotation to ensure continuity in leadership, management and day-to-day operations.
A number of electronic initiatives have been undertaken to facilitate claim registration and review. This is a move towards the use of digitized resources whenever possible which, in turn, will contribute to more efficient service delivery. It also supports the goal of increased proactive compliance on the part of claimants who will have more tools available to them on the Commission's website.
