ARCHIVED - Hazardous Materials Information Review Commission - Report
 This page has been archived.
This page has been archived.
Archived Content
Information identified as archived on the Web is for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. It has not been altered or updated after the date of archiving. Web pages that are archived on the Web are not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards. As per the Communications Policy of the Government of Canada, you can request alternate formats on the "Contact Us" page.
2012-13
Report on Plans and Priorities
Hazardous Materials Information Review Commission
The original version was signed by
The Honourable Leona Aglukkaq
Minister of Health
Table of Contents
Section I: Organizational Overview
- Raison d’être
- Responsibilities
- Strategic Outcome and Program Activity Architecture (PAA)
- Organizational Priorities
- Risk Analysis
- Planning Summary
- Expenditure Profile
- Estimates by Vote
Section II: Analysis of Program Activities by Strategic Outcome
Section III: Supplementary Information
Section IV: Other Items of Interest
President’s Message
I am pleased to present to the Parliament of Canada, and to Canadians, the Hazardous Materials Information Review Commission's Report on Plans and Priorities 2012-13. This report outlines where the Commission will focus its efforts over the next three years to address issues related to trade secret protection and hazard communications, and take into account the needs of its various stakeholders.
The Commission will continue to align its activities in three strategic directions: proactive compliance, knowledge transfer and strategic partnerships. This will be achieved through enhanced integrated planning to ensure the best use of financial and human resources, to address short and long term outcomes, and to monitor success through performance measurement.
First, the Commission will meet its mandate to register claims for trade secret protection and correct associated Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs) and product labels. In building proactive compliance, HMIRC will continue to develop ways to increase claimants' support and knowledge at the start of the claim review process. This will enable efficiencies that will make corrected health and safety information available to workers sooner.
Second, by disseminating the knowledge it has collected, HMIRC will be able to extend the use and application of its expertise. This requires ongoing effort within the Commission to enhance the organization and translation of information, as well as interaction with others outside the Commission involved with hazard communication, in order to contribute up-to-date and effective results for workers and industry.
Third, partnering with like-minded organizations will be an economical way to serve mutual goals. With limited resources, it makes sense to collaborate when possible. In pursuing this end, the Commission will continue the information gathering, analysis and discussion necessary for building partnerships.
I am convinced the activities the Commission has outlined for the planning period will make a positive impact on workers, employers, suppliers and others concerned with health and safety in the workplace. In fulfilling its national role within the Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS), HMIRC continues to contribute to industry competitiveness and compliant health and safety information. Finally, HMIRC is committed to working with its stakeholders and government to ensure fiscal responsibility in these times of restraint and derive increasing value for Canadians.
Sharon Watts
President & Chief Executive Officer
Section I: Organizational Overview
Raison d’être
The Hazardous Materials Information Review Commission provides a single mechanism under federal, provincial and territorial legislation to protect the trade secrets of companies that supply or use hazardous materials, and ensures that Canadian workers who handle such materials have all the information they need to do so safely.
Responsibilities
The Commission enables companies to protect their trade secrets and, at the same time, ensures that MSDSs for products with trade secrets used by workers in Canada disclose complete and accurate information to reduce workplace-related illness and injury. The Commission's activities are key components of WHMIS, which was created in 1987 through a consensus between workers, industry and government. The success of WHMIS depends on cooperation among all these partners. All three groups play an integral part in ensuring that chemical products are used as safely as possible in Canadian workplaces.
WHMIS requires that suppliers provide employers with MSDSs and product labels which detail information on the hazards of materials sold for use in Canadian workplaces. The employers, in turn, provide these MSDSs and labels to workers and, as well, training on how to handle the products safely. A product's MSDS must fully disclose all hazardous ingredients in the product, its toxicological properties, the safety precautions workers need to take when using the product, treatment required in the case of injury, and other pertinent information.
When a supplier introduces a product and wants to protect the identity or concentration of one or more of the hazardous ingredients, according to the Hazardous Materials Information Review Act (HMIRA), the company needs to apply to HMIRC for an exemption from the requirement to list all hazardous ingredients on the product's MSDS. Once HMIRC registers a claim, the product can be made available in the marketplace without disclosing the confidential business information. The Commission then evaluates the claim and issues a decision on its validity and, to protect workers, verifies the compliance of the MSDS with the Hazardous Products Act and Controlled Products Regulations.
When an employer purchases a product and wants to protect the identity and/or concentration of any hazardous ingredients, or the name and the supplier of the product, according to the HMIRA, the company also needs to apply to HMIRC for an exemption. In this case, in addition to issuing a decision on the claim's validity, the Commission evaluates the MSDS and, if necessary, the label, against the requirements of either the Canada Labour Code, for federally regulated employers, or the relevant provincial or territorial occupational health and safety regulations.
Where areas of non-compliance are identified, the Commission offers claimants the opportunity to make corrections through voluntary compliance undertakings. If the claimant chooses not to accept the undertaking, the Commission issues formal orders obligating the claimant to make the changes.
In cases where there are disputes that cannot be resolved, HMIRC convenes independent boards to hear appeals from claimants or affected parties challenging decisions and orders or from affected parties challenging undertakings signed by claimants and accepted by HMIRC.
In addition, HMIRC responds to requests from federal, provincial or territorial government health and safety officials for information about claims for exemption to help these officials administer and enforce their WHMIS obligations.
Governance
The Commission's governance structure is based on collaboration between government, industry and workers. The Council of Governors provides strategic advice and guidance to the Commission and makes recommendations to the Minister of Health. It consists of up to 18 members representing key stakeholders across all jurisdictions:
- 1 representing the federal government,
- up to 13 representing the provincial and territorial governments,
- 2 representing workers,
- 2 representing industry (1 representing suppliers and 1 representing employers).
The Commission's President and Chief Executive Officer is appointed by the Governor in Council to supervise and direct the organization's day-to-day activities. The President is accountable to Parliament through the Minister of Health.
Strategic Outcome(s) and Program Activity Architecture
Organizational Priorities
| Priority | Type1 | Strategic Outcome(s) and/or Program Activity(ies) |
|---|---|---|
| Advance compliance with WHMIS standards | Ongoing | Strategic Outcome |
| Status | ||
|
Why is this a priority? The Commission is committed to safeguarding chemical trade secrets and improving compliance with WHMIS standards in hazard communications to the benefit of claimants, workers and industry. Proactive compliance creates greater efficiency in the claim process, makes worker health and safety information available faster and ultimately reduces the risk of injury in the workplace. Plans for meeting the priority
|
||
| Priority | Type | Strategic Outcome(s) and/or Program Activity(ies) |
|---|---|---|
| Increase stakeholder knowledge of chemical hazard classification and communication | Ongoing | Strategic Outcome |
| Status | ||
|
Why is this a priority? Increased translation and dissemination of the Commission's scientific knowledge will contribute to improved worker health and safety information. Plans for meeting the priority
|
||
| Priority | Type | Strategic Outcome(s) and/or Program Activity(ies) |
|---|---|---|
| Leverage the Commission's knowledge, expertise and resources through key partnerships | Ongoing | Strategic Outcome |
| Status | ||
|
Why is this a priority? Strategic partnerships will allow for innovative, cost-effective and practical solutions to improve knowledge and understanding of, and proficiency in, hazard communications, as well as compliance with WHMIS/GHS standards. Plans for meeting the priority
|
||
| Priority | Type | Strategic Outcome(s) and/or Program Activity(ies) |
|---|---|---|
| Enhance management accountability | Ongoing | Internal Services |
| Status | ||
|
Why is this a priority? Renewed accountability will focus the Commission's attention and resources in order to efficiently, effectively and economically align with short and long term outcomes. Plans for meeting the priority
|
||
Risk Analysis
Operational Context
Workers, industry and government agree on the importance of preventing illnesses and injuries from hazardous materials in Canadian workplaces. In order to help achieve this goal, WHMIS was created through the adoption of complementary and interlocking legislation across federal, provincial and territorial jurisdictions. WHMIS requires suppliers, including manufacturers, importers and distributors, and employers, to provide health and safety information about the chemicals produced or used in Canadian workplaces.
As part of the WHMIS initiative, the Hazardous Materials Information Review Act and related regulations also came into force. This legislation established the Hazardous Materials Information Review Commission (HMIRC), an independent agency with a quasi-judicial role. HMIRC provides the mechanism in Canada to protect the confidential business information of chemical suppliers and employers, and to ensure accurate and complete health and safety information is available to workers.
Risks and Opportunities
The Commission will continue its efforts to increase proactive compliance with WHMIS standards. The earlier MSDSs and labels are compliant, the earlier workers have access to corrected health and safety information. Various HMIRC initiatives will contribute to this, including enhanced guidance materials and streamlined processes, especially digital formats, for claimants. These efforts require the support of strengthened information technology and information management systems.
Strategic partnerships, forged between the Commission and other interested organizations, will provide new opportunities to effectively and economically share expertise on hazard communication with stakeholders. To achieve this end, the Commission will collect, organize and analyze information in order to identify potential partners and the nature of future collaborations. The Commission's modest resources dictate a measured approach to this commitment.
The Commission will maintain its commitment to integrated planning, aligning resources with activities, outcomes and strategic directions. With a renewed governance structure in place, the ongoing implementation of infrastructure will ensure sound management of financial and human resources, communications, information management and information technology, and enhance accountability and benefits for Canadians.
Planning Summary
Financial Resources ($ thousands)
| 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 |
|---|---|---|
| 4,523 | 4,523 | 4,523 |
Human Resources (FTEs)
| 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 |
|---|---|---|
| 42 | 42 | 42 |
| Performance Indicators | Targets |
|---|---|
| Percentage of claimants who have applied corrected trade secret protected material safety data sheet (MSDS) information to other MSDSs | 50% |
| Estimated financial value of confidential business information protected under the Hazardous Material Information Review Act | $100M |
| Program Activity | Forecast Spending 2011-12 |
Planned Spending | Alignment to Government of Canada Outcomes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | |||
| Statutory Decision and Compliant Information | 2,797 | 2,804 | 2,804 | 2,804 | Healthy Canadians |
| Stakeholder Engagement and Strategic Partnerships | 538 | 543 | 543 | 543 | Healthy Canadians |
| Total Planned Spending | 3,347 | 3,347 | 3,347 | ||
| Program Activity | Forecast Spending 2011-12 |
Planned Spending | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | ||
| Internal Services | 1,200 | 1,176 | 1,176 | 1,176 |
| Total Planned Spending | 1,176 | 1,176 | 1,176 | |
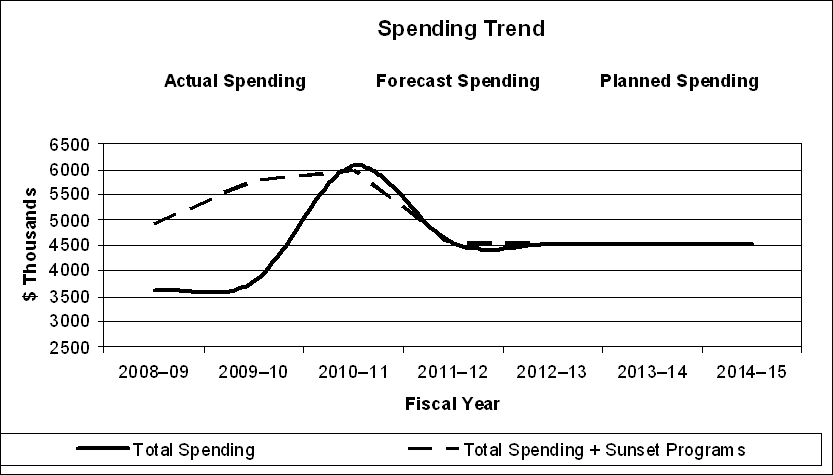
Expenditure Profile
Estimates by Vote
For information on our organizational appropriations, please see the 2012-13 Main Estimates publication.
Section II - Analysis of Program Activities by Strategic Outcome
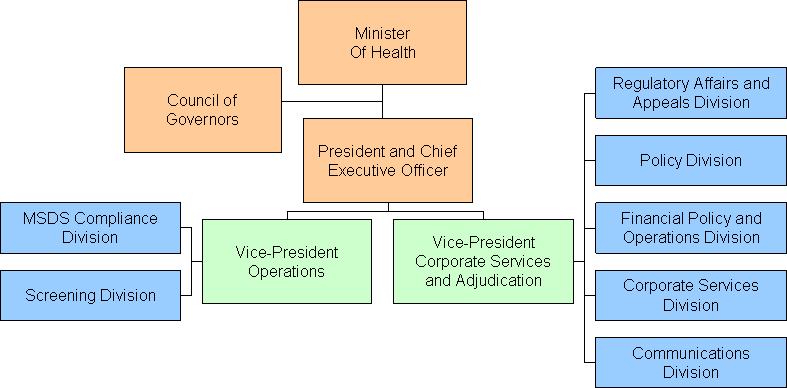
Strategic Outcome: Chemical trade secrets are protected and required health and safety information in Canadian workplaces is compliant.
Program Activity: Statutory Decisions and Compliant Information
Program Activity Description
The Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) requires chemical manufacturers, importers, distributors, and employers to provide cautionary labelling and material safety data sheets (MSDSs) for every controlled product produced, used or intended for use by workers in Canadian workplaces. Pursuant to the Hazardous Materials Information Review Act, the Hazardous Materials Information Review Commission has the mandate to make decisions on the validity of claims for exemption from disclosure requirements under WHMIS, while ensuring that associated health and safety information made available to Canadian workers is compliant with the WHMIS standards. Specifically, to fulfill its program requirements, the Commission registers claims, issues decisions on claim validity and compliance, offers claimants an opportunity to comply voluntarily and when necessary, orders claimants to take actions to bring MSDSs and/or labels into compliance. In carrying out this program, the Commission fosters proactive compliance. It assists claimants in respecting relevant statutory requirements by providing the information, knowledge, tools and support they need to submit complete and accurate claims and bring associated MSDSs and/or labels into compliance.
Financial Resources ($ thousands)
| 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 |
|---|---|---|
| 2,804 | 2,804 | 2,804 |
Human Resources (FTEs)
| 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Program Activity Expected Results | Performance Indicators | Targets |
|---|---|---|
| Claimants submit valid claims | Percentage of claims found to be valid on review | 100% |
| Claimants are proactively compliant with Workplace Hazardous Material Information System requirements | Average number of violations in material safety data sheets of record | 4.5 |
Planning Highlights
In order to achieve the Expected Results, the Commission will focus on the following areas:
The establishment of a compliance baseline to inform future proactive approaches.
In order to develop proactive approaches to claim validity and improved WHMIS compliance, HMIRC will analyze claim information to determine where in the claim process it can best introduce its expertise on hazardous classification and communication. This
will also help to identify the most critical areas. Once a more complete compliance baseline is in place, the Commission will have an enhanced capability to foster proactive compliance in claimants.
Claimants are provided with the knowledge, tools and information to be WHMIS compliant.
As part of WHMIS, the Commission is responsible for communicating WHMIS requirements to claimants and verify that submitted MSDSs are accurate and compliant. To this end, it will pursue various means to share
information from its knowledge base, and it will continue to invest in the development of tools to best convey and apply this information. The sooner health and safety information is compliant, the better for Canadian workers.
Ongoing improvements to claim processing.
The Commission will continue to process claims efficiently and effectively, and to introduce improvements that further enhance various stages of the process, such as an e-Submission pilot
Program Activity: Stakeholder Engagement and Strategic Partnerships
Program Activity Description
The exclusive work completed by the Commission enables it to gather unique information and data holdings on hazard communications under the Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System in terms of completeness, accuracy, comprehensibility and accessibility. Through partnerships, the Commission attempts to more fully a) mine, b) test and compare and c) share its knowledge so as to improve hazard communications for Canadian industry and Canadian workers. It also uses this knowledge to improve the understanding and proficiency of interested domestic and international public bodies in developing hazard communication approaches, tools and standards. Consequently, this program supports the establishment of mutually beneficial partnerships that contribute to the creation and distribution of information and knowledge that enhance the safe handling of hazardous chemicals.
Financial Resources ($ thousands)
| 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 |
|---|---|---|
| 543 | 543 | 543 |
Human Resources (FTEs)
| 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Program Activity Expected Results | Performance Indicators | Targets |
|---|---|---|
| Improved knowledge and proficiency of hazard communications | Percentage of participants who increased knowledge of hazard communication due to outreach activity | 75% |
| Percentage of participants at outreach activity who used increased knowledge to improve hazard communication | 25% |
Planning Highlights
In order to achieve the Expected Results, the Commission will focus on the following areas:
Explore and identify stakeholder interest in forming mutually beneficial partnerships.
With its unique expertise, and taking into account the limited resources available, the Commission will leverage its knowledge and experience and that of partners to maximize the achievement of outcomes by pursuing mutually beneficial partnerships. As a preliminary step in the development of partnerships, HMIRC will seek
opportunities to engage informally with other relevant organizations.
Share information to improve stakeholder knowledge of hazard communications.
The exclusive work the Commission performs allows it to gather unique information. HMIRC will place greater emphasis on analyzing, synthesizing and sharing its knowledge and information of a non-confidential nature so as to enhance the completeness, accuracy, comprehensibility and accessibility of hazard communications to the
benefit of stakeholders.
Internal Services
Internal Services are groups of related activities and resources that are administered to support the needs of programs and other corporate obligations of an organization. At HMIRC these groups are: Management and Oversight Services; Legal Services; Communications Services; Human Resources Management Services; Financial Management Services; Information Management Services; Information Technology Services; Acquisition Services; and Travel and Other Administrative Services. Internal Services include only those activities and resources that apply across an organization and not to those provided specifically to a program.
Financial Resources ($ thousands)
| 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 |
|---|---|---|
| 1,176 | 1,176 | 1,176 |
Human Resources (FTEs)
| 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | 12 | 12 |
Planning Highlights
The Commission will extend and further implement its Integrated Plan over 2010-2016, concentrating especially on operational components in support of its strategic directions and identified outcomes. These efforts will confirm key strategic functions and priorities, allocate resources accordingly, and concentrate on the delivery of outputs to ensure alignment with and contribution to outcomes.
The Commission's volunteer participation in a horizontal audit on the Management, Resources and Results Structure (MRRS) Policy will be followed up with implementation of recommendations in 2012-13. The monitoring and refining of evaluation tools will help to measure the impact of products and services and, ultimately, contribute to greater efficiency, effectiveness and economy. Evidence-based information will be used to report on results, demonstrate value to Canadians, as well as support improvement and engagement towards management of excellence.
The Commission will complete and refine tools and guidelines related to human resources management, financial management, information technology (IT) and information management (IM). In addition, IT and IM will provide the requisite support to new initiatives, such as e-submissions; a strategic communications plan will assist efforts at outreach and knowledge translation; the implementation of the Budget Management Framework will clarify reporting and accountability; and Commission participation in the Shared Services Working Group and Steering Committee for Finance will ensure small agency concerns are taken into consideration.
Section III - Supplementary Information
Financial Highlights
| % Change | Future-Oriented 2012-13 |
Future-Oriented 2011-12 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Expenses | 0% | 5,280,233 | 5,263,614 |
| Total Revenues | 0% | (569,621) | (569,615) |
| Net Cost of Operations | 0% | 4,710,612 | 4,693,999 |
| % Change | Future-Oriented 2012-13 |
Future-Oriented 2011-12 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Total assets | -9% | 184,514 | 203,116 |
| Total liabilities | -6% | 1,066,403 | 1,136,061 |
| Equity | -5% | (881,889) | (932,945) |
| Total | -9% | 184,514 | 203,116 |
Future-Oriented Financial Statements
List of Supplementary Information Tables
All electronic supplementary information tables found in the 2012-13 Report on Plans and Priorities can be found on the Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat's web site:
- Greening Government Operations (GGO)
- Sources of Respendable and Non-Respendable Revenue
- Upcoming Internal Audits and Evaluations over the next three fiscal years
Section IV - Other Items of Interest
Organizational Contact Information
Mail:
Hazardous Materials Information Review Commission
427 Laurier Avenue West, 7th floor
Ottawa, Ontario
K1A 1M3
Telephone: 613-993-4331
Facsimile: 613-993-5016
Website: www.hmirc-ccrmd.gc.ca
E-mail: hmirc-ccrmd@hc-sc.gc.ca
Footnotes
1 Type is defined as follows: previously committed to - committed to in the first or second fiscal year prior to the subject year of the report; ongoing - committed to at least three fiscal years prior to the subject year of the report; and new - newly committed to in the reporting year of the RPP or DPR.